Why is solar power not widely used, even though it has become more accessible and cost-effective?
With the obvious benefits of lowering your electricity bill and carbon footprint, solar technology can be the face of tackling climate change and shifting towards cleaner energy.
Sadly, not all are jumping on the solar bandwagon. Although many areas in North America have ample sunlight, solar power only makes up less than 5% of the total energy usage.
Strange, right? With the sun’s unlimited energy waiting to be used, its adoption should be booming.
Here, we’ll look into why solar technology, despite its apparent benefits, isn’t as widely used as expected. We’ll also explore the obstacles slowing its uptake and discuss practical ways to overcome these barriers.
Before that, let us talk about why you should consider solar power.
Why Consider Solar Power?

As the call for environmental responsibility grows louder and energy costs become less stable, solar energy becomes a source of hope and practicality.
Below, we highlight the three major promises solar power brings that makes it a compelling option for anyone looking to make a positive impact.
1. Energy Independence And Cost Savings
Are you feeling the impact of rising electricity bills? In Alberta, the rise from 16 to 32 cents per kilowatt-hour within just a few months last 2023 demonstrates the unpredictable nature of energy costs.
With electricity rates rising significantly, many seek stable alternatives, and solar power offers a promising solution.
Since solar power lets you generate electricity, you become less grid-dependent and enjoy low and stable energy costs, unaffected by market fluctuations.
2. Environmental And Health Benefits
For an average household using 10,632 kWh annually, switching to home solar is like planting an acre of trees annually or eliminating the need to burn over 8,000 pounds of coal.
Furthermore, adopting solar energy can decrease air pollutants like nitrous oxides and sulfur dioxide.
The health benefits are also clear: fewer CO2 emissions mean reduced cases of heart and respiratory issues and fewer workday absences due to sickness.
3. Leverage Technological Advances Over Traditional Fuels
The solar industry has achieved remarkable advancements, now boasting a 31.6% energy conversion efficiency compared to its previous 24.4%. The cost of solar panels has decreased by 50% in recent years, along with government incentives and rebates.
Unlike fossil fuels, which run out and are detrimental to the environment during extraction, solar energy has a sustainable energy supply, making it a key player in our journey toward sustainable living.
Evidently, solar power is a smart move toward energy independence, environmental stewardship, and economic savings.
With fluctuating electricity rates, solar energy offers a stable and predictable alternative. Not only does it provide cost savings, but it also contributes to a healthier planet and society.
Advancements in solar technology have also dramatically increased efficiency and affordability, making solar power a practical choice over traditional systems.
Still, why isn’t it as popular as it should be? Let us now answer this question.
Why Is Solar Power Not Widely Used? What’s Holding Back
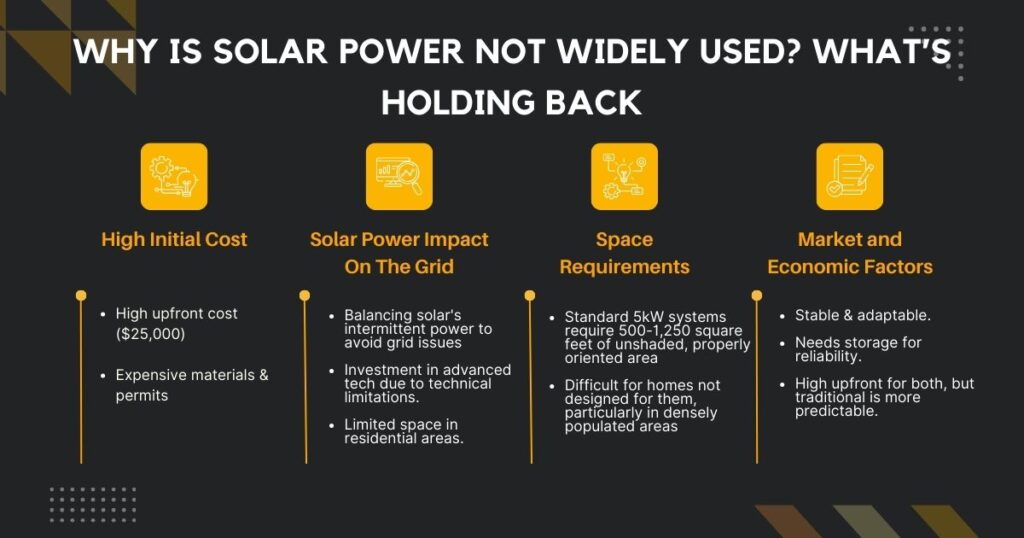
High Initial Costs
On average, solar panels’ upfront cost is around $25,000. Although solar prices have decreased over the last decade, this cost is still expensive for most potential consumers.
Why is the price still high?
Silicon in solar cells is the main factor. Silicon, while cheaper in electronics, is costly to process in the solar industry.
While emerging alternatives like cadmium telluride provide more affordable solar cell options, permits, installation, and equipment costs remain significant, making solar power a substantial financial commitment.
Solar Power Impact On The Grid
Integrating solar power into the grid presents significant challenges. Remember that solar energy isn’t constant; it changes based on factors like time of day and weather.
With this, grid operators balance the grid and solar power to avoid problems like equipment damage or blackouts. Balancing is tricky because solar energy doesn’t flow around easily like fossil fuels.
The following technical challenges are the most common in grid-tied systems:
- Voltage Regulation: Rapid changes in solar power can cause the voltage to fluctuate, potentially harming appliances and affecting people’s health.
- Short Circuit Risks: Connecting solar systems to the grid increases the chance of short circuits, posing safety risks and potential equipment damage.
- Unintentional Islanding: Parts of the grid with solar power might keep running even when they’re supposed to shut down, risking damage and safety.
- Frequency Stability: Solar power can cause the grid’s frequency to change, which needs to be managed carefully to keep things running smoothly.
- Reactive Power Control: As more solar plants connect to the grid, managing voltage with reactive power becomes more challenging, requiring careful coordination to maintain reliability.
As solar penetration increases, the grid must evolve with more sophisticated technology and management strategies, demanding significant investments like solar storage systems and inverters, leading to additional expenditures.
Space Requirements
One challenge with solar panel systems is their space requirements in residential areas. Typically, a standard 5kW system demands 500-1,250 square feet (46-116 square meters) of space, not shaded and correctly oriented. The problem is that not all homes are built to fit solar panels.
If roof space is insufficient, you can opt for a ground installation. However, this can still be difficult in dense residential areas, where finding enough open, sunny space is often difficult.
Market and Economic Factors
Traditional energy sources like coal, hydro, and nuclear already have well-established infrastructure to ensure power stays stable regardless of time and weather.
With this, traditional energy can provide energy security and a consistent supply to meet market demand. In addition, coal, hydro, and nuclear plants can adapt their power output as needed and transport their energy or fuel, unaffected by external factors.
Solar, on the other hand, is inherently intermittent, heavily dependent on the sun, and can fluctuate due to weather conditions, making it less reliable without adequate storage to ensure consistent, on-demand energy.
Concerning economic factors, solar power is comparable to other conventional energy sources. Both have high start-up and development costs. Still, traditional power plants, while high in maintenance, are better understood and predictable than emerging solar technologies.
What Efforts Are Made to Make Solar Power Widely Used?
As the urgency for sustainable energy solutions intensifies, concerted efforts are being made to boost the adoption and efficiency of solar power.
These efforts include the planned use of new technologies and the creation of helpful government rules, both of which aim to make solar energy a common power source. Here’s how these efforts are unfolding:
1. Enhanced Solar Modules

- Advancements in solar technology have led to modules that exceed 600W, targeting efficiencies of up to 25%. This progress allows for higher energy output using fewer panels.
- Additionally, advanced tracking technologies change the orientation of the panels to get the most sunlight. Doing so could increase energy yields by up to 144% by 2030 and make solar installations more practical for many.
Digitization:
- Digital integration in solar power projects is streamlining costs and enhancing efficiency. Advanced data analytics and AI can optimize solar system design and placement, reducing development and operational costs.
- One example of advanced data analytics is this web mapping app that provides automated estimates of solar potential and daily global insolation for any location in Canada.
Perovskite Solar Cells:
- Emerging as a frontier technology, perovskite cells promise to significantly elevate conversion efficiencies, potentially nearing 40%, at costs lower than those of conventional silicon cells.
- Despite facing challenges such as durability and environmental safety, these cells represent a promising direction in solar technology.
2. Supportive Government Policies for Solar Energy
Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) and Incentives:
- Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS), or Renewable Electricity Standards (RES), are policies for boosting renewable energy generation. They guide operators of renewable energy operations to create and sustain plans for conserving and reclaiming their project sites.
- Like RPS, most financial incentives are government-backed and aim to encourage business and household sectors to adopt clean energy usage. For example, the Clean Technology Manufacturing ITC offers a 30% tax credit for eligible properties from 2024 to 2031.
Net Metering Policies:
- These policies enable solar energy producers to sell surplus power back to the grid, providing financial returns and supporting the economic case for solar investments.
Public Awareness and Infrastructure Support:
- Increased funding for solar research, streamlined permitting procedures, and advocacy for public and community solar projects are pivotal governmental actions.
- These initiatives enhance public engagement, facilitate solar project implementation, and signify a collective movement toward a sustainable and renewable energy future.
What Is The Future Of Solar Energy?
Predicting solar energy’s evolution over the next decade is challenging, yet its role in the global energy landscape is expected to expand significantly.

The fact that Canada aims for 90% clean energy by 2030 emphasizes the importance of solar power in the future.
Key trends shaping solar’s future include ongoing cost reductions and making solar more accessible.
As technological advancements continue, achieving more efficient and clean energy is possible. In developing countries, this could significantly improve electricity access and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
The transportation sector is also poised to integrate more solar solutions, such as solar-powered and solar-assisted electric vehicles.
Goals for renewable energy and financial incentives will help the industry grow and generate new ideas. Finally, rules and laws supporting solar power will make it more popular worldwide.
A Bright And Sustainable Future With Panel Upgrade Experts
Dive into the bright future of solar energy with Panel Upgrade Experts!
We’re here to guide you toward sustainability that benefits your health and wallet.
Embrace the opportunity to achieve significant savings and be a beacon of environmental responsibility. Our expertise will streamline your solar journey toward efficiency and energy conservation.
Ready to modernize? Contact Panel Upgrade Experts and start saving now!
Final Thoughts
Solar power is growing, but not without challenges. High upfront costs, efficient grid integration, finding enough space for installations, and competition against traditional energy sources are still up.
However, with a strong push for new technology and government incentives and policies, solar is becoming a more tempting investment.
If you want to make a switch, save on energy bills, and support a cleaner environment, get involved today! With Panel Upgrade Experts, you’ll be a part of a cleaner, more sustainable future.
FAQs
Why use solar panels?
Solar panels harness the sun’s energy, a clean and renewable power source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions. They can significantly lower electricity bills, offer energy independence, and increase property value.
What are the barriers to using extensive solar?
Barriers to widespread solar energy adoption include high initial installation costs, the need for significant space for panels, variability in solar energy production due to weather conditions, and integration challenges with the existing power grid.
The public also needs to know about the benefits of solar energy and understand any possible financial incentives that could encourage its use.
What is the future of solar power in Alberta, Canada?
Alberta’s future in solar power looks promising due to its ample sunny days and the province’s goal to diversify its energy sources and reduce carbon emissions.
There is also an increasing investment in residential and commercial solar installations due to government incentives and rebates to decrease the costs of solar technologies.
Are solar panels expensive?
The upfront cost of solar panels can be significant, but it has decreased over the years due to technological advancements and economies of scale.
While the initial investment may be high, solar panels typically offer long-term savings on electricity bills, tax incentives, and possible rebates.
Over time, these savings can offset the initial costs, making solar panels a financially viable option for many property owners.


